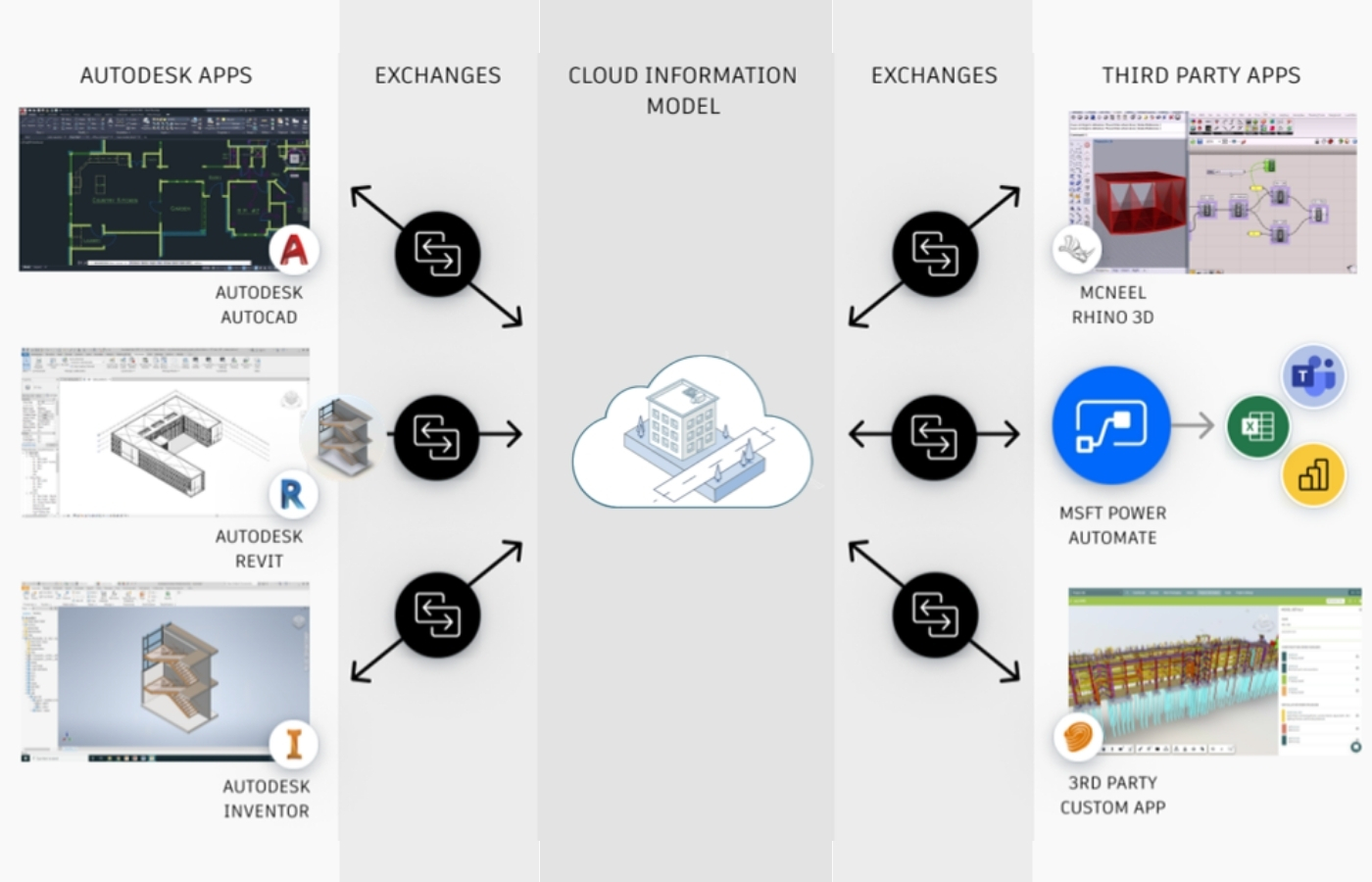
Enterprise Platforms
Application Development
Data & AI
Digital Twin
Cloud
Solution Engineering
Extended Development Centre
ACC Integration with Enterprise Applications
Autodesk Fusion Manage PLM with ERP Integration
ACC Implementation Services
Design Automation for CAD & BIM Applications
BIM 360 & Construction Cloud Migration Services
4D Schedule Visualization
5D Cost Visualization
View and explore what our research team is up to. Experience the depth and demonstration of live applications.